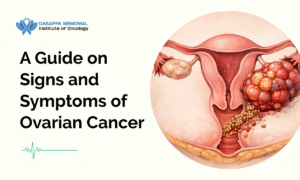
Ovarian cancer signs and symptoms are often very subtle, and I hear this from patients all the time: “Doctor, I thought it was just normal.” Bloating, mild pelvic pain, and feeling tired. These things are easy to ignore when life is busy. But when these symptoms keep coming back or don’t feel right for your body, they matter more than we think.
Let me explain what to watch for, how ovarian cancer usually shows up, and when it’s important to get checked so you feel more confident listening to your body.
Medical Disclaimer
The information provided in this blog is intended for general awareness and educational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Every cancer case is unique, and treatment decisions should always be made in consultation with a qualified oncologist or healthcare professional. If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms or has been diagnosed with cancer, please seek personalised medical guidance from a specialised cancer care provider.
Key Points at a Glance
- Ovarian cancer symptoms are often vague and easily misattributed
- Early symptoms may be subtle and persistent
- Advanced or late-stage symptoms are more intense and disruptive
- No single screening test exists; clinical evaluation is essential
- Multiple diagnostic tests help doctors make an accurate diagnosis
- Early detection dramatically improves outcomes and treatment success
- Awareness, risk understanding, and timely care are key
What Is Ovarian Cancer?
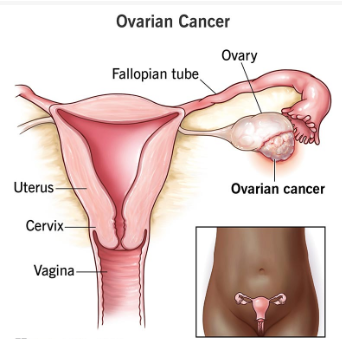
Ovarian cancer begins in one or both ovaries, the small, almond-shaped organs in the female reproductive system that produce eggs and hormones. It occurs when abnormal cells in the ovaries begin to grow and multiply uncontrollably. These cells can eventually form a tumour and spread to nearby tissues or distant organs if not detected early.
One of the reasons ovarian cancer is so challenging to diagnose early is that symptoms often don’t show up until the disease has spread beyond the ovaries into the abdomen or pelvis.
Why Early Detection Is Difficult
Unlike some cancers that have clear early warning signs or reliable screening tests, ovarian cancer often develops without obvious symptoms. Many women don’t notice anything unusual until the cancer has already progressed.
Additionally, routine exams like Pap smears don’t detect ovarian cancer, which makes solely relying on routine checks insufficient for early diagnosis.
That’s why staying alert to persistent changes, even if they seem mild, is so important.
Ovarian Cancer Early Signs
Ovarian cancer early signs may be subtle, and most women with these early symptoms don’t realise they could signal cancer. Symptoms are often dismissed as digestive discomfort, menstrual changes, or stress.
Common early symptoms include:
- Persistent bloating or swelling of the abdomen
- Pain or discomfort in the pelvis or lower belly
- Feeling full quickly or loss of appetite
- Frequent or urgent urination
- Changes in bowel habits, such as constipation or diarrhoea
These symptoms may be mild at first, but the key is persistence; they occur more often and last longer than typical gas or menstrual discomfort.
Understanding Symptoms vs Everyday Issues
It’s easy to confuse ovarian cancer symptoms with common health issues. Here’s a simple comparison to help you notice patterns:
| Symptom | Often Mistaken For | Possible Ovarian Cancer Sign |
|---|---|---|
| Bloating | Gas, digestion issues | Persistent bloating not relieved by normal remedies |
| Pelvic pain | Menstrual cramps | New pelvic discomfort that doesn’t fade |
| Appetite changes | Stress or diet | Regular feeling of fullness quickly |
| Urinary frequency | Fluid intake | Unexplained frequent urination |
| Bowel habit changes | Irritable bowel syndrome | Ongoing constipation or diarrhea |
When a symptom doesn’t go away, it’s worth talking to your healthcare provider.
Less Common Early Symptoms
Some women may notice:
- Fatigue
- Back pain
- Abdominal discomfort
- Mild menstrual changes
These can feel nonspecific, and that’s why I always encourage women not to ignore patterns that feel “different” for them personally, especially if they persist for weeks.
Ovarian Cancer Late-Stage Symptoms
When ovarian cancer advances, symptoms often become more obvious and severe. These ovarian cancer last stage symptoms may include:
- Significant abdominal swelling due to fluid buildup
- Severe pelvic or abdominal pain
- Persistent nausea or loss of appetite
- Rapid weight loss
- Bowel obstruction or changes
- Shortness of breath (if cancer spreads to the lungs)
In advanced stages, cancer can spread beyond the ovaries to the lymph nodes, abdominal organs, or even distant organs like the liver or chest.
Why Symptoms Often Appear Late
Because the ovaries are located deep inside the pelvis, small tumours might not cause obvious physical signs until they grow or spread. This “silent” progression is one of the major reasons ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a later stage.
Reasons for Ovarian Cancer and Risk Factors
The exact reasons why ovarian cancer develops are not fully understood, but doctors have identified several risk factors that increase the likelihood of the disease:
| Risk Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Age (over 60) | Most common in older women |
| Genetic mutations (BRCA, Lynch) | Inherited gene changes raise risk |
| Family history of ovarian/breast cancer | Increases personal risk |
| Endometriosis | Can elevate risk |
| Never been pregnant | Slightly higher risk compared to pregnancy history |
Your doctor may recommend genetic counselling or testing if you have a strong family history.
How Ovarian Cancer Is Detected
If a woman has symptoms that raise concern, doctors start with a clinical evaluation, which may include a physical exam and pelvic check. Because no definitive early screening exists yet, evaluation focuses on symptoms and diagnostic tests.
Which Tests Are Used To Diagnose Ovarian Cancer
There isn’t a single perfect test, but a combination helps doctors reach an accurate diagnosis.
Common tests include:
- CA-125 blood test: Measures a protein that is often higher in ovarian cancer, though it can be elevated due to other conditions as well.
- Pelvic ultrasound: Looks for masses or abnormalities.
- CT scan or MRI: Provides detailed imaging of the abdomen and pelvis.
- PET scan: Helps detect cancer spread.
- Biopsy or surgical evaluation: Tissue samples confirm diagnosis.
Research is ongoing to develop blood tests that detect ovarian cancer earlier and more accurately, which could dramatically improve early diagnosis in the future.
Stages of Ovarian Cancer
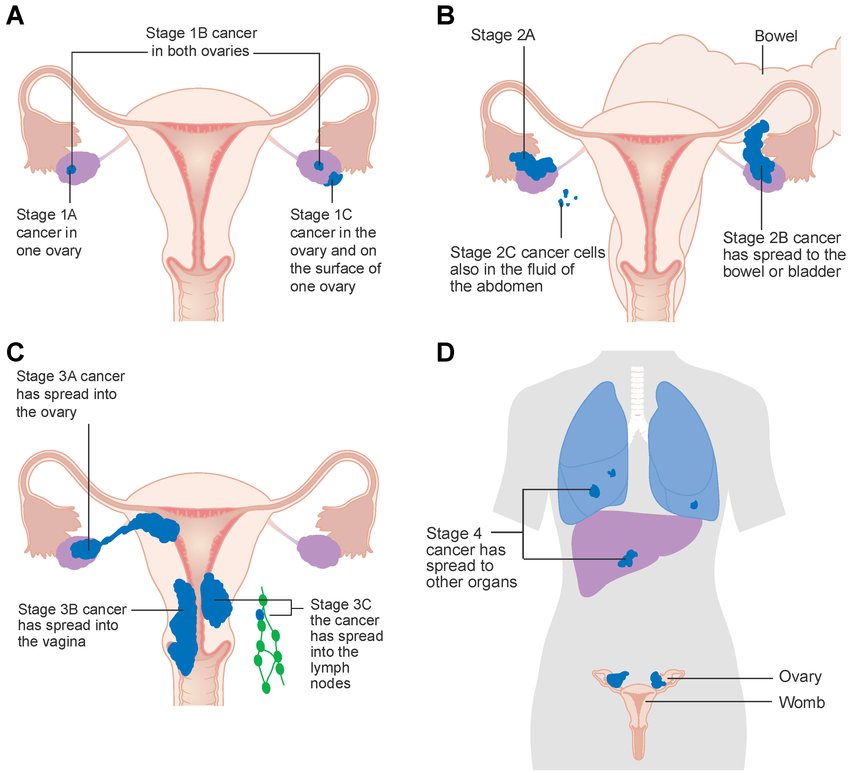
Cancer is staged to describe how far it has spread. Staging guides treatment decisions and helps predict outcomes.
| Stage | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Stage I | Cancer is confined to one or both ovaries |
| Stage II | Spread to nearby pelvic organs (uterus, fallopian tubes) |
| Stage III | Spread within the abdominal cavity or lymph nodes |
| Stage IV | Spread to distant organs (lungs, liver) |
Each stage may be divided into sub-categories depending on tumour size and exact spread.
What Are The Treatment Options For Ovarian Cancer
Treatment depends on the stage, general health, and specifics of the tumour:
- Surgery: Often the first step, removing as much of the tumour as possible.
- Chemotherapy: Drugs to kill cancer cells, given before or after surgery.
- Targeted therapy; Drugs that attack specific cancer cell characteristics.
- Hormonal therapy: Used in certain cancer types.
- Follow-up care: Regular checkups to monitor for recurrence.
Radiation therapy is rarely used but may be considered in specific situations.
Living With and After Treatment
Recovery is not just about medical treatment; emotional support, mental resilience, and lifestyle changes all contribute to overall well-being. Ongoing follow-up appointments ensure any new symptoms are checked promptly and care remains personalised.
When to See a Doctor
You should consult a doctor if:
- Symptoms persist for more than a few weeks
- Pain or discomfort is unusual or unexplained
- You notice swelling or changes in urination or bowel habits
- There’s abnormal bleeding or discharge
Early evaluation gives you the best chance to catch ovarian cancer before it advances.
Choosing the Right Care Center
Ovarian cancer requires specialised care. A gynecological cancer treatment hospital in Bangalore offers focused expertise, advanced diagnostics, and multidisciplinary treatment.
Access to experienced oncologists, surgeons, and support services improves both survival and quality of life. Choosing the right centre is a crucial step.
Final Thoughts
Becoming familiar with ovarian cancer signs and symptoms helps you take charge of your health and get medical attention before small changes become big problems. Staying aware, tracking changes, and choosing expert care make all the difference.
With compassionate, advanced care available at a specialised cancer hospital in Bangalore, like Dasappa Cancer Hospital, you are never alone on this journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Does ovarian cancer have early symptoms?
Yes, but they are often subtle and easily mistaken for other issues like digestive discomfort.
2. Can a Pap smear detect ovarian cancer?
No, Pap smears screen for cervical, not ovarian, cancer.
3. Is there a reliable ovarian cancer screening test?
Currently, no single test can reliably screen all women; evaluation uses a combination of tests instead.
4. Can ovarian cancer be cured?
When detected early, treatment can be very effective. Later stages require more intensive therapy and careful monitoring.
Reference:
1. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4447-ovarian-cancer
Image:
2. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4447-ovarian-cancer